

Shows that both CD28 and CTLA-4 can associate with the serine/threonine phosphatase PP2A and indicates that PP2A might negatively regulate T-cell activation.Ĭefai, D. The CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors associate with the serine/threonine phosphatase PP2A. T cell antigen CD28 binds to the GRB-2/SOS complex, regulators of p21ras. T-cell antigen CD28 interacts with the lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by a cytoplasmic Tyr(P)–Met–Xaa–Met motif. Binding of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase to CD28 is required for T-cell signalling. Analysis of CD28 cytoplasmic tail tyrosine residues as regulators and substrates for the protein tyrosine kinases, EMT and LCK. p56 Lck and p59 Fyn regulate CD28 binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, growth factor receptor-bound protein GRB-2, and T cell-specific protein-tyrosine kinase ITK: implications for T-cell costimulation. T lymphocyte costimulation mediated by reorganization of membrane microdomains. Single cell analysis reveals regulated hierarchical T cell antigen receptor signaling thresholds and intraclonal heterogeneity for individual cytokine responses of CD4 + T cells. T cell activation determined by T cell receptor number and tunable thresholds. CD28 costimulation promotes the production of TH2 cytokines. Bcl-x, a Bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death.
Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. The duration of antigenic stimulation determines the fate of naive and effector T cells. Antigen decoding by T lymphocytes: from synapses to fate determination. Mutations in the antigen-binding site of the TCR that significantly decrease or increase the half-life of the association between TCR with MHC–peptide complex were shown to result in impaired T-cell activation, indicating an optimal interaction time. Efficient T cell activation requires an optimal dwell-time of interaction between the TCR and the pMHC complex. High- and low-potency ligands with similar affinities for the TCR: the importance of kinetics in TCR signaling. Ligand recognition by αβ T cell receptors.
#CTLA4 TCEL SERIAL#
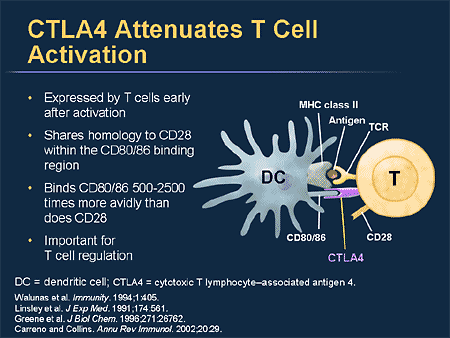
Serial triggering of many T-cell receptors by a few peptide–MHC complexes. Valitutti, S., Muller, S., Cella, M., Padovan, E. Evidence that a single peptide–MHC complex on a target cell can elicit a cytolytic T cell response. Sykulev, Y., Joo, M., Vturina, I., Tsomides, T. A new analysis of allogeneic interactions. Phosphorylation of the two tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic tail of CTLA-4 is not necessary for CTLA-4 to deliver its inhibitory signal.īretscher, P. The role of CTLA-4 in tolerance induction and its capacity to impart inhibitory function to regulatory CD25 +/CD4 + T cells is controversial.ĬTLA-4 functions both by scavenging CD80/86 ligands away from CD28 and by direct negative signalling to T cells. This latter function might also be controlled by the C-terminal proline-rich region of CD28.Ĭytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) ligation raises the threshold needed for T-cell activation and arrests T-cell-cycle progression. The Y170 in the cytoplasmic tail of CD28 seems important for BCL-X L upregulation and might contribute to CD28-mediated cytokine production and proliferation. On TCR stimulation, CD28 signalling quantitatively augments TCR-mediated signals, as well as activating independent pathways. The numbers of T-cell receptors (TCRs) engaged, as well as the time of interaction with the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)–peptide complexes, determine whether T-cell activation occurs.Ībsence of Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity results in augmented interleukin-2 (IL-2) production and proliferation by normal T cells, and increased production of T H2-type cytokines following priming.ĬD28 crosslinking reduces the number of TCRs that need to be engaged, as well as the time required for T cells to interact with antigen, and enhances the magnitude of the T-cell response.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
